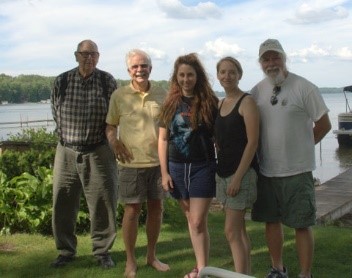LAKE SCIENCES
CO-CHAIRS | LEN KLEIN & KAREN BAKER
Mission Statement
The Lake Science Team has already begun sampling with the help of our new interns, Brian Stitt, and Mike Schwartz. Brian is a student in NMC’s Water Quality Studies and Mike is a cost-shared intern from the Benzie Conservation District. Sharing an intern with Benzie Conservation District is a new endeavor we are trying this year.
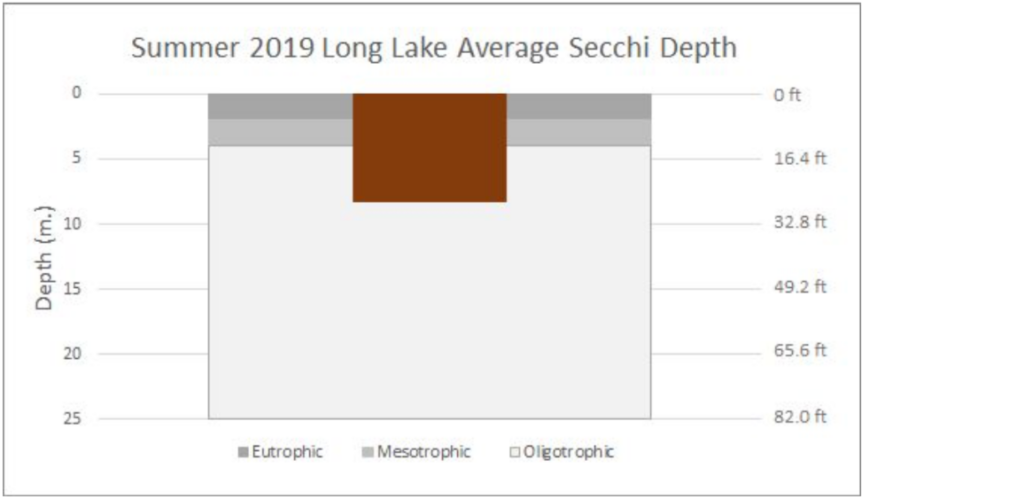
Last year, our Team found only minor variations in our study parameters from previous years. Our sampling still shows the overall quality of Long, Mickey and Ruth Lakes to be good but as the lake levels fell, the clarity and other parameters were negatively affected.
The key concerns that we identified over the course of the summer of 2024 stem from weather and natural conditions from the low ice coverage in winter, and lack of rainfall. These are beyond our control. The largest change in our lakes was the water level; all lake levels were lower than their long-term averages. While we received slightly higher than normal precipitation over this winter, the lakes are still lower than normal for this time of year. Our lake levels are dependent on precipitation and groundwater infiltration with evaporation responsible for most water loss.
Other items of concern we attribute to recreational activities and human causes. The potential introduction of additional invasive species such as the New Zeeland Mud Snail and Water Lettuce from recreational activities is always a major concern. Proper boat and equipment washing is essential to reduce the spread of these and other invasives. This is the goal of the new boat wash committee.
Proper riparian setbacks and shoreline buffer zones planted with native plants help control erosion and runoff from property. A shoreline with a buffer zone of 20 to 30 feet with proper native plants can reduce surface runoff of sediments by 70 to 90 percent and other pollutants by 25 to 60 percent. Have your soil evaluated to determine amendment requirements and utilize natural products away from the shoreline.
Aging and improperly maintained septic systems are another way pollutants enter the lake. Remember that what goes down the drain will end up in your septic system then filtered through the soil, eventually entering our groundwater. Be a good lake steward and make sure your septic system is operating efficiently.
Water Chemistry Sampling Sites 2019
Water quality sampling sites on Long Lake, 1997-2019
LAKE |
SAMPLE SITE |
LATITUDE |
LONGITUDE |
|
Long Lake |
#1 |
44.70383° |
-85.74432° |
|
#2 |
44.72473° |
-85.75612° |
|
|
#3 |
44.47409° |
-85.76453° |
|
|
Mickey Lake |
#1 |
44.73257° |
-85.76640° |
|
#2 |
44.73217° |
-85.76867° |
|
|
Ruth Lake |
#1 |
44.69483° |
-85.76255° |
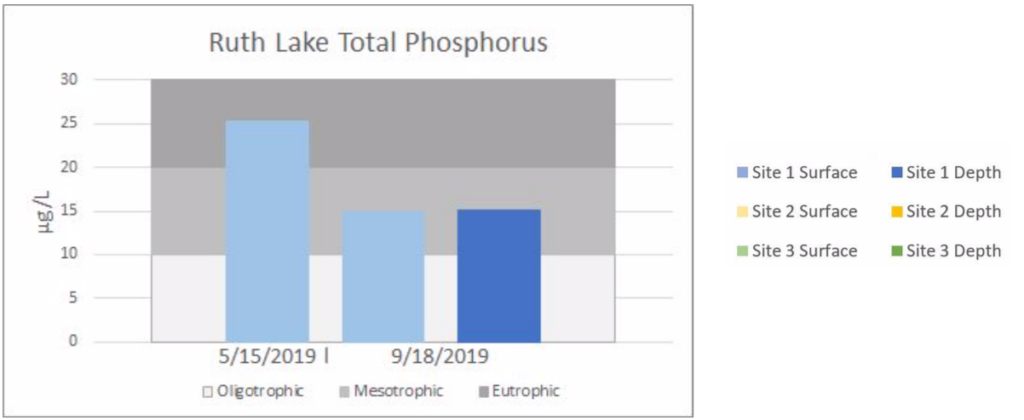
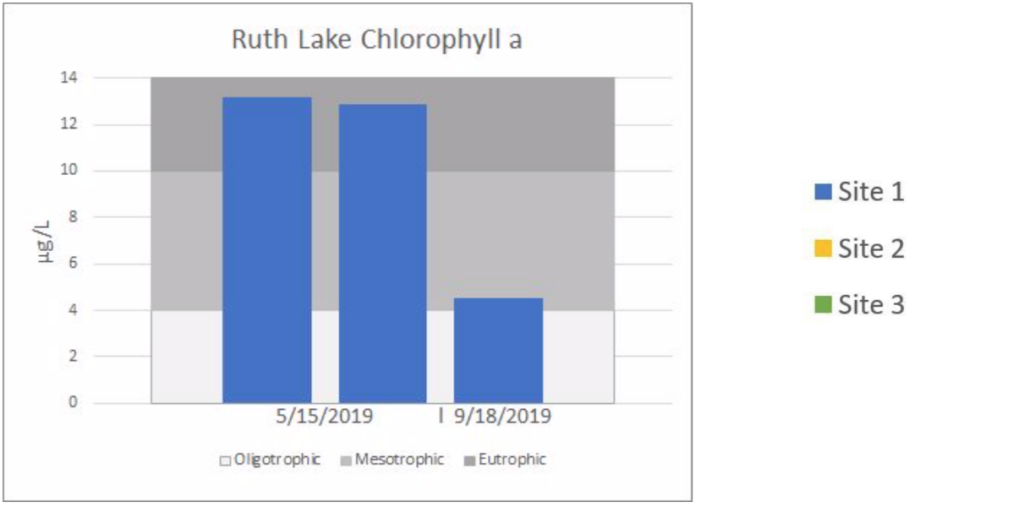
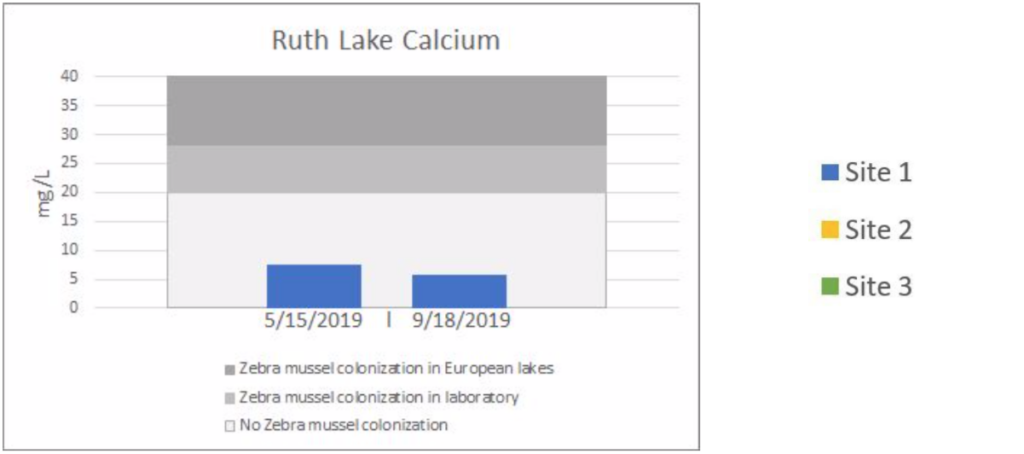
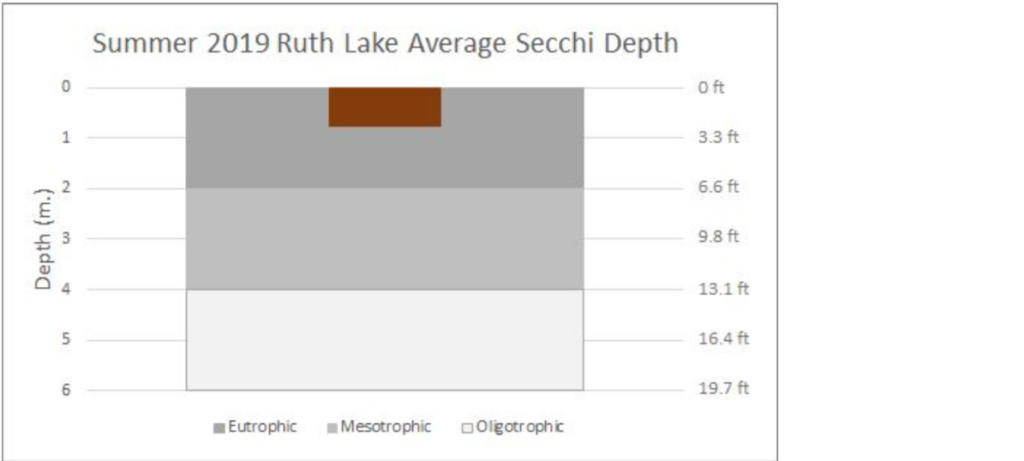
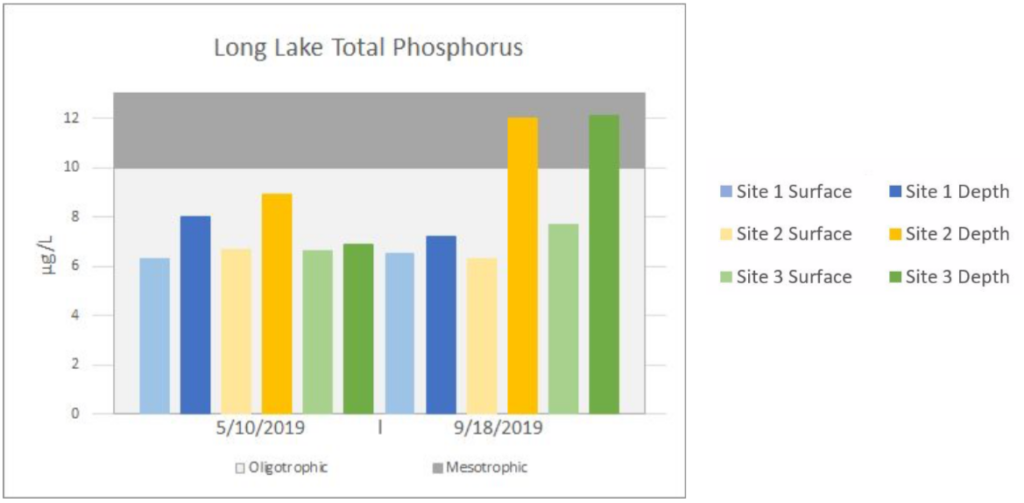
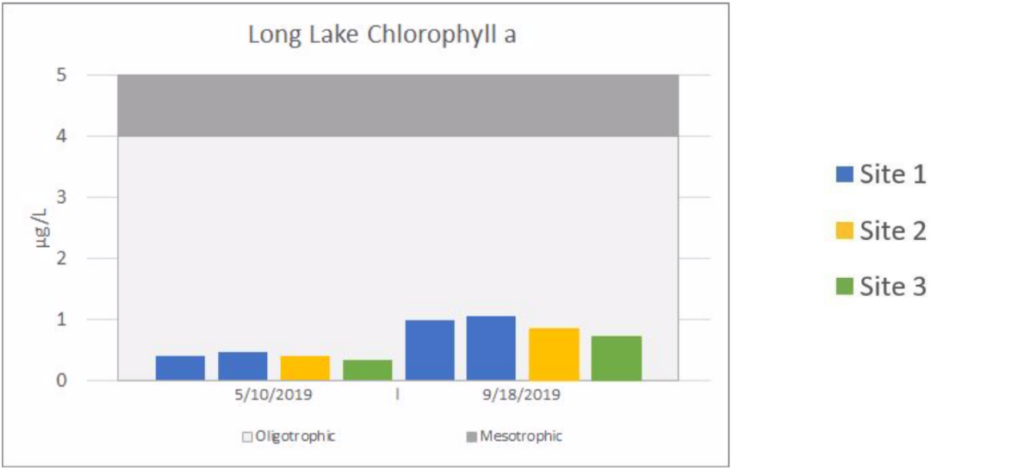
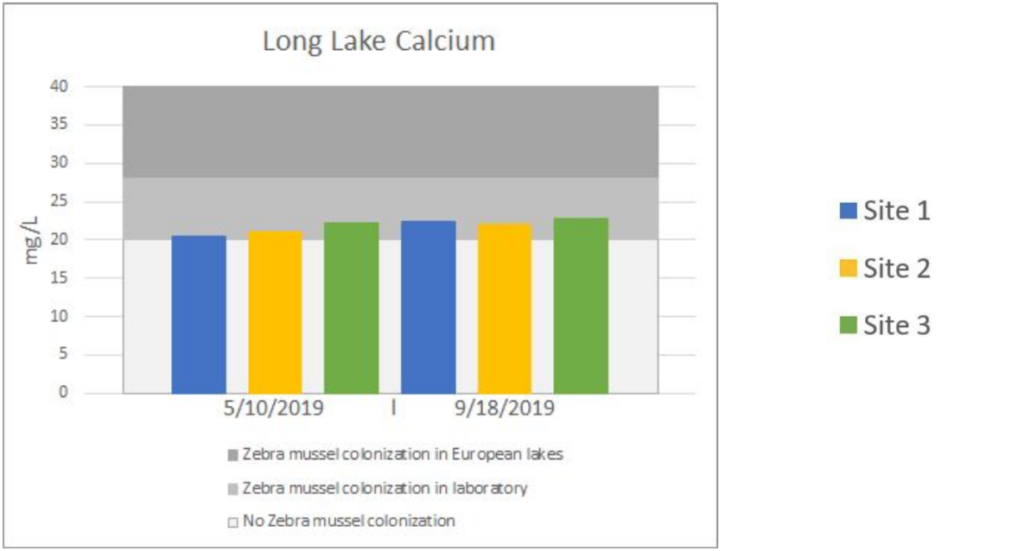
The charts below are a summarization of the water chemistry data collected in 2019. This map show where the samples have been collected.
Lake Water Quality Monitoring | LONG LAKE
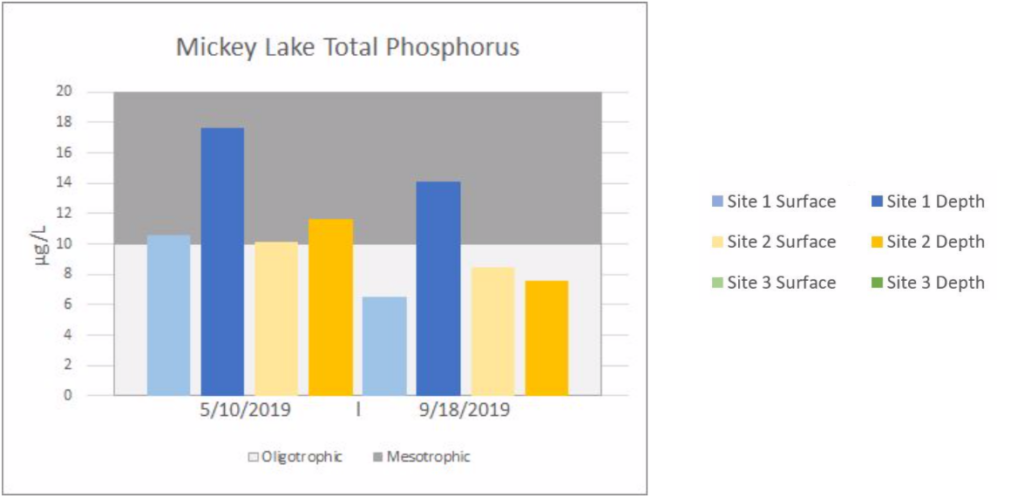
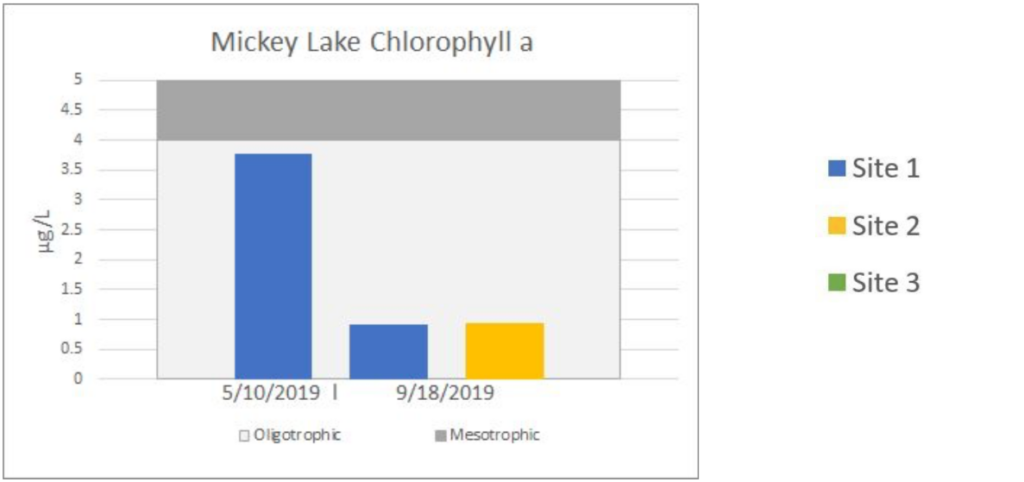
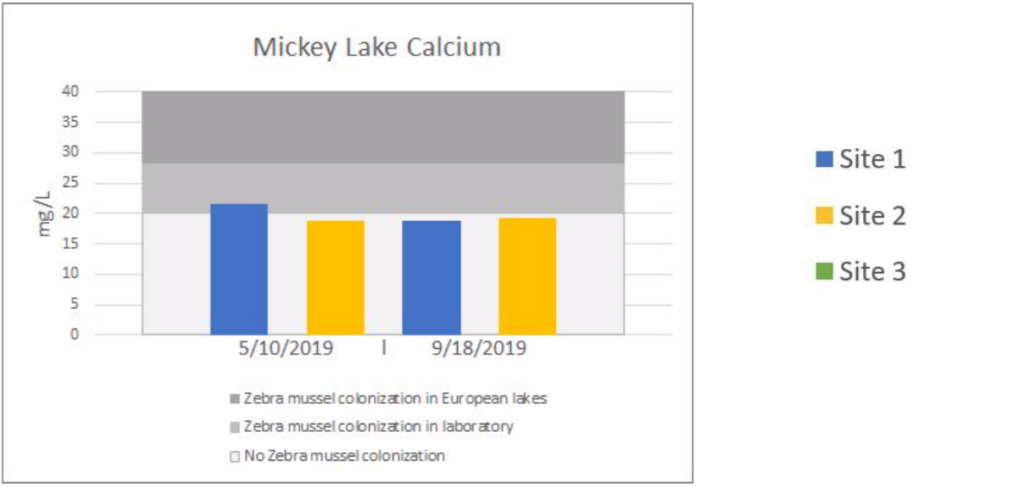
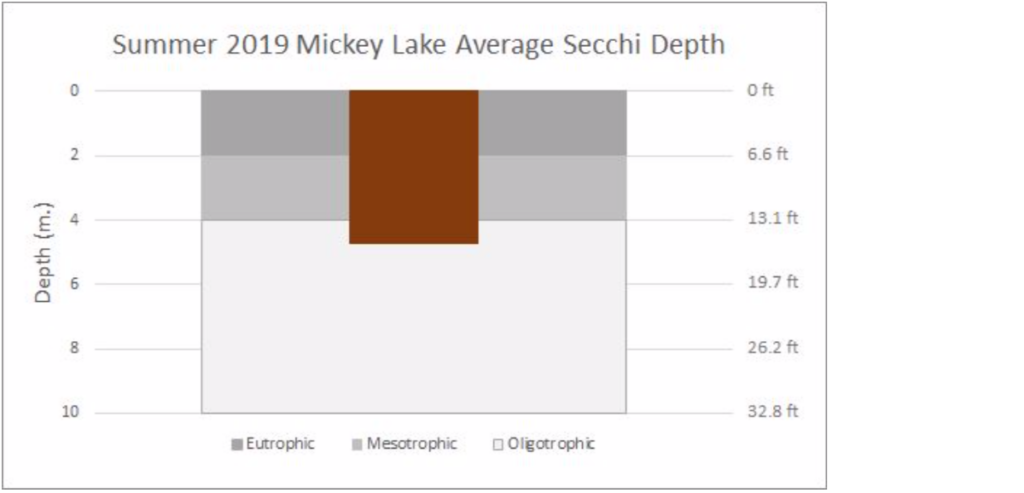
Lake Water Quality Monitoring | MICKEY LAKE
Lake Water Quality Monitoring | RUTH LAKE